Exercises
Task 01
Install G++ and Clang, then compile the provided file hello.cpp.
Use the following flags when compiling:
-std=c++17 -Wall -Wextra -O2
Next, set up Boost on your system and compile the provided file hello_boost.cpp.
Boost is quite common and provides you a set of useful C++ libraries.
Some of its content is even promoted into the C++ standard library.
Task 02
Run Clang on the provided file vec.cpp using the following command:
clang -std=c++17 -Xclang -ast-dump -fsyntax-only -Wno-vexing-parse vec.cpp
Clang will parse the input file and display its abstract syntax tree (AST).
In the bottom half of the output you'll find the function declaration of main followed by its CompoundStmt.
Take a close look at its children and compare the resulting AST with the input code.
Notice any oddities — something that looks counter intuitive?
As you can see, there are multiple different ways of initialisation in C++. Check out the corresponding section at cppreference.
Task 03
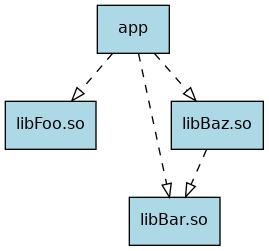
The directory task03 hosts four subdirectories, libFoo, libBar, libBaz, and app.
Each folder prefixed with lib represents a library and contains a header plus a source file.
Furthermore, the library libBaz.so depends on libBar.so.
app contains a single source file providing a main function.
It depends on all three libraries.
- Model this project structure using CMake
- Be sure to set the C++ standard to C++17 and enable warnings (
-Wall -Wextra) - The default build type should be Release
CMake itself is a build system generator. You can choose from a variety of target build systems.